|
Back to 2011 Program
Modification of the Wise Pattern Skin Resection for Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction in Patients with Macromastia or Severe Breast Ptosis
William Samson, MD, Jamie Schwartz, MD, Joseph H. Dayan, MD, Mark L. Smith, MD, Mark R. Sultan, MD.
St. Luke's-Roosevelt Hospital, New York, NY, USA.
BACKGROUND
Immediate breast reconstruction in women with macromastia or severe breast ptosis presents challenges in matching the skin envelope with the reconstructed breast mound. Mastectomies performed with a Wise pattern skin resection may be used, but often result with mastectomy flap necrosis. A modified version of the Wise pattern, designed to reduce the risk of native breast skin necrosis, is introduced in this study.
METHODS
The Wise pattern skin resection has been modified so that the horizontal incisions are staggered. The medial limb of the skin resection is the same as a traditional Wise pattern and lies along the inframammary fold. The lateral limb, however, begins at the apex of the vertical skin resection and is carried out laterally across the lateral aspect of the breast. This avoids an ischemic T-junction at the base of the traditional Wise pattern
RESULTS
Eleven patients underwent immediate breast reconstruction using the modified Wise pattern technique. Four had bilateral breast reconstruction and seven had unilateral reconstruction with this method (n=15 breasts). In the unilateral reconstruction group, two patients had simultaneous contralateral reconstruction using a skin resection pattern other than the modified Wise, four patients underwent simultaneous contralateral balancing procedures and one balancing procedure was performed in the delayed setting. Both autologous and prosthetic reconstruction techniques were used: Abdominal free flaps (n=8), tissue expanders (n=5), latissimus dorsi flap-expander (n=2). There were no instances of autologous flap failure or implant infection. Three patients (n= 3 breasts) had minor partial thickness epidermolysis (<2cm margin around incision). There were no cases of full-thickness skin necrosis in any of the modified Wise pattern breasts.
CONCLUSIONS
The modified Wise pattern mastectomy is a safe and effective method of removing excess native breast skin when performing immediate breast reconstruction in patients with macromastia or severe breast ptosis. The standard Wise pattern introduces risk of mastectomy flap necrosis, typically at the distal ends of the superiorly based skin flaps (the T-junction). The modified Wise pattern described eliminates the T-junction by moving the lateral skin excision superiorly. While this results in a more visible lateral scar, it generally lies within the lower pole and does not interfere with precise shaping of the breast mound. 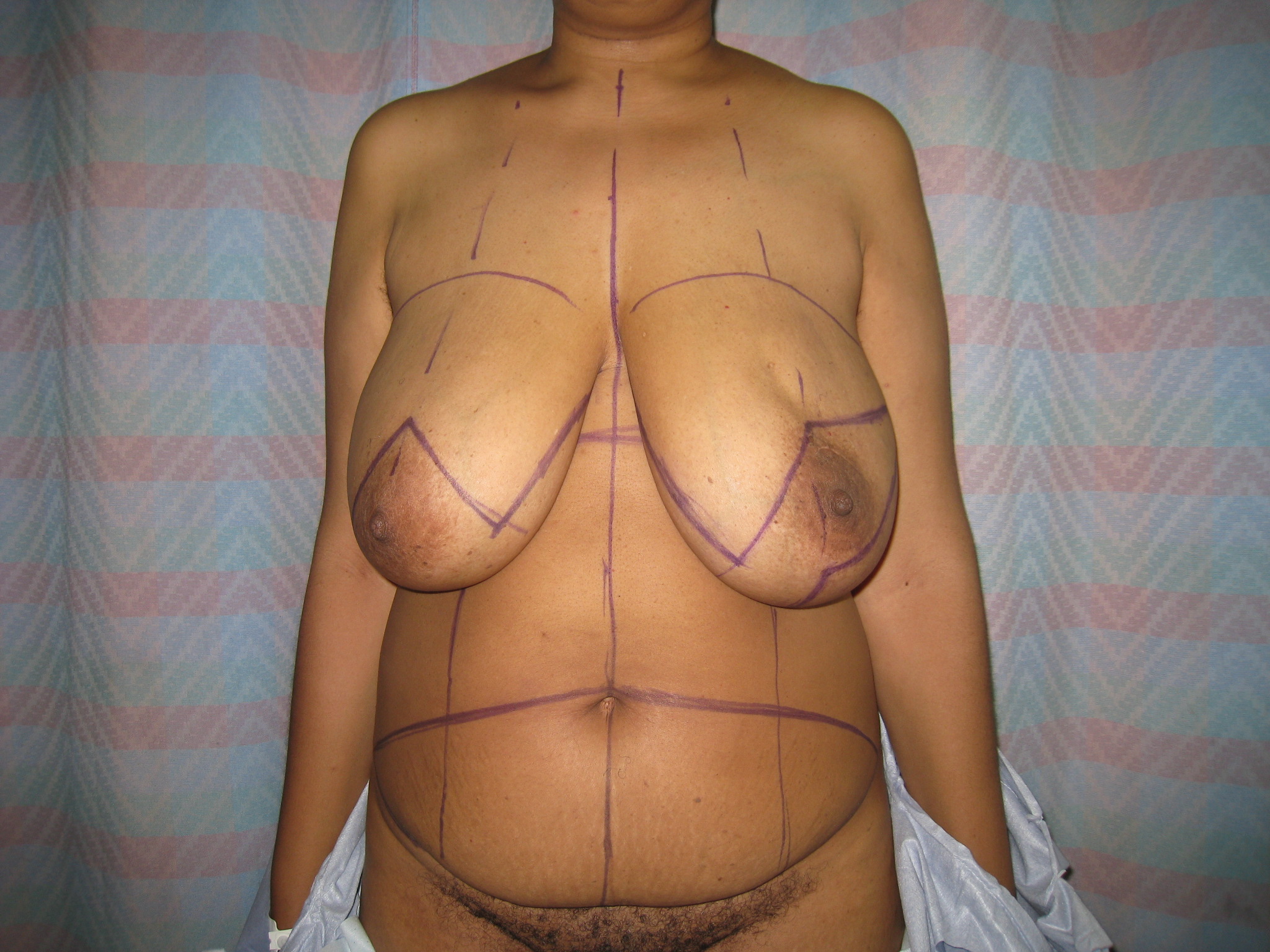 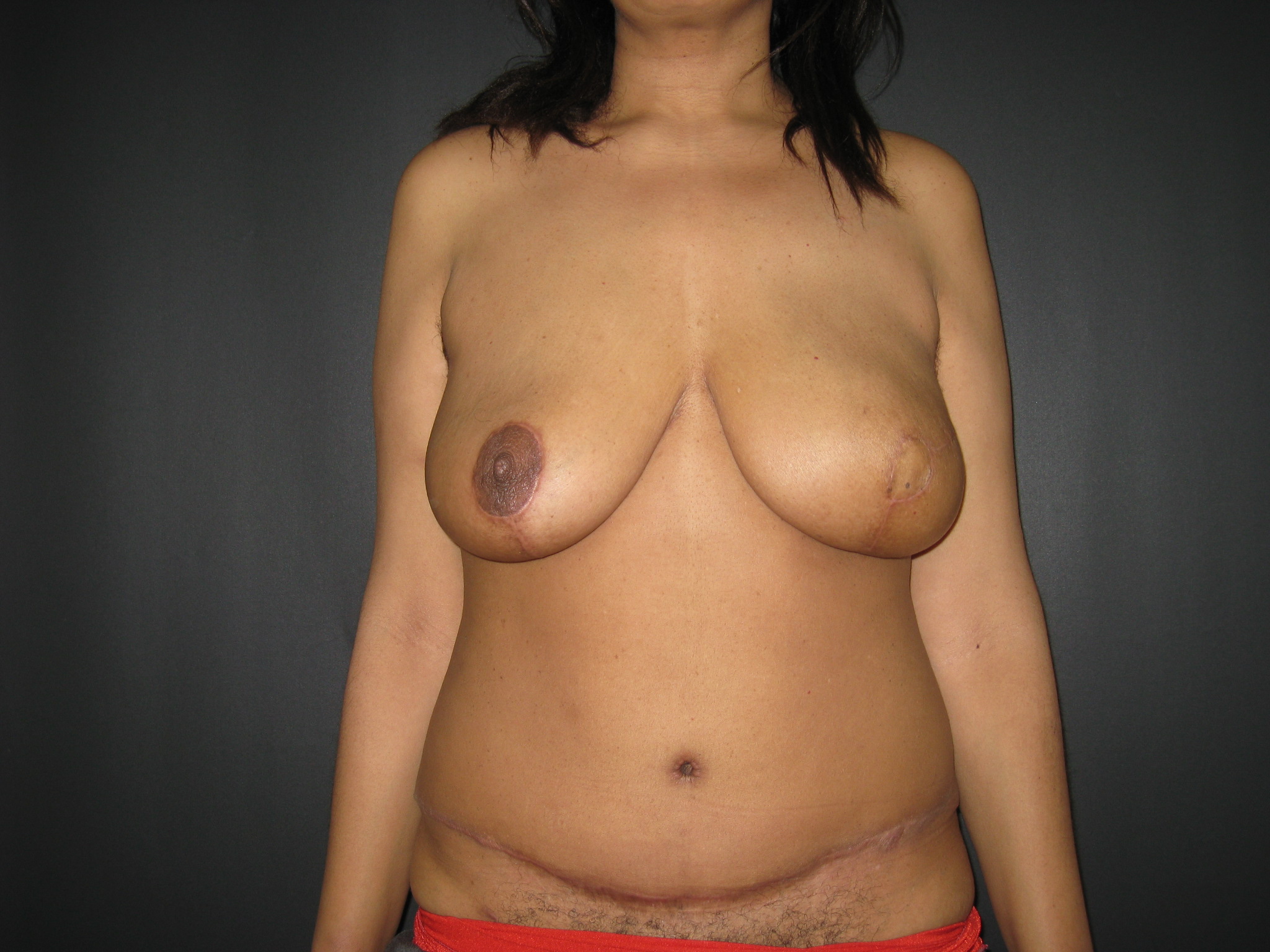
Back to 2011 Program
|







