|
|
 |
Back to 2011 Program
The Lateral Inframammary Fold Incision for Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy: Outcomes from Over 50 Immediate Implant-Based Breast Reconstructions
Keith M. Blechman, MD, Chaya Levovitz, BA, Amber A. Guth, MD, Deborah M. Axelrod, MD, Richard L. Shapiro, MD, Mihye Choi, MD, Nolan S. Karp, MD.
New York University, New York, NY, USA.
BACKGROUND: Nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM) is rapidly gaining popularity as its safety and efficacy continue to be supported. NSM decreases scar burden and leaves the nipple-areola complex (NAC) intact, affording superior aesthetics compared to traditional skin-sparing reconstructions. The lateral inframmammary fold (LIMF) incision provides adequate access and eliminates an anterior scar, making this incision cosmetically preferable to other approaches. Here we present our experience with NSM through a LIMF incision, with immediate implant-based reconstruction.
METHODS: We retrospectively reviewed 52 consecutive nipple-sparing mastectomies via a LIMF incision from June 2008 to April 2011 that underwent immediate implant-based reconstruction, with or without use of a tissue expander. Breasts were gently infiltrated with hemostatic anesthetic solution, and sharp dissection was preferred to avoid thermal injury to the mastectomy flap. Intraoperative subareolar biopsies were performed. Three-dimensional (3D) photographs were obtained prior to mastectomy and after reconstruction was complete. 3D parameters included volume, antero-posterior projection, and ptosis (defined by the distance from a set superior point to the inferior breast pole).
RESULTS: Average age was 47 years. Mean follow-up time was 11 months. Therapeutic mastectomy was performed in 23% of breasts, and prophylactically in 77%. Tissue expansion was used in 93%, and Alloderm was used in 65%. Fat grafting (average 92cc) was performed if residual contour deformities remained. If sentinel lymph node biopsy was performed, it was possible via the LIMF incision in 75%. Three nipples (6%) suffered partial necrosis. Two mastectomy flaps (4%) underwent operative debridement, one which required a salvage latissimus dorsi flap. There were no hematomas, seromas, or locoregional recurrences. 3D analysis demonstrated larger (196 vs 248cc), more projected (80 vs 90mm), and less ptotic breasts (146 vs 134mm) (p<0.01).
CONCLUSIONS: Excellent outcomes can be achieved following NSM through a LIMF incision using immediate expander/implant reconstruction. There is no anterior scar burden, and sentinel lymph node biopsy can be performed without a counter-incision. NAC and mastectomy flap survival rates are high. NSM reconstruction via this approach can create larger, more projected, and less ptotic breasts. 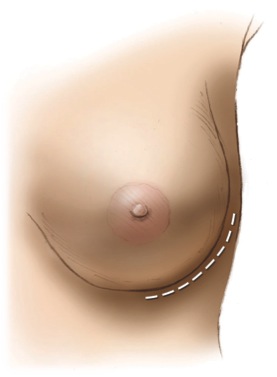
Back to 2011 Program
|








