|
|
|
|
|
Back to 2015 Annual Meeting
Breast Reconstruction Using Contour Fenestrated AlloDerm: Does Improvement in Design Translate to Improved Outcomes?
Jordan D. Frey, MD1, Michael Alperovich, MD1, Katie E. Weichman, MD2, Stelios C. Wilson, MD1, Alexes Hazen, MD1, Pierre B. Saadeh, MD1, Jamie P. Levine, MD1, Mihye Choi, MD1, Nolan S. Karp, MD1.
1NYU Langone Medical Center, New York, NY, USA, 2Montefiore Medical Center, New York, NY, USA.
Background: Acellular dermal matrices are commonly utilized in implant-based breast reconstruction and continue to evolve. New contour fenestrated Alloderm is sterilely processed, crescent-shaped, and includes prefabricated fenestrations, but has not yet been evaluated in comparison with previous generations of ADM.
Methods: All patients undergoing implant-based breast reconstruction were identified. Patients were stratified by type of implant coverage: aseptic ADM, sterile, ready-to-use ADM, contour fenestrated ADM, or total submuscular coverage. Results were compared with p-values less than 0.05 being deemed significant.
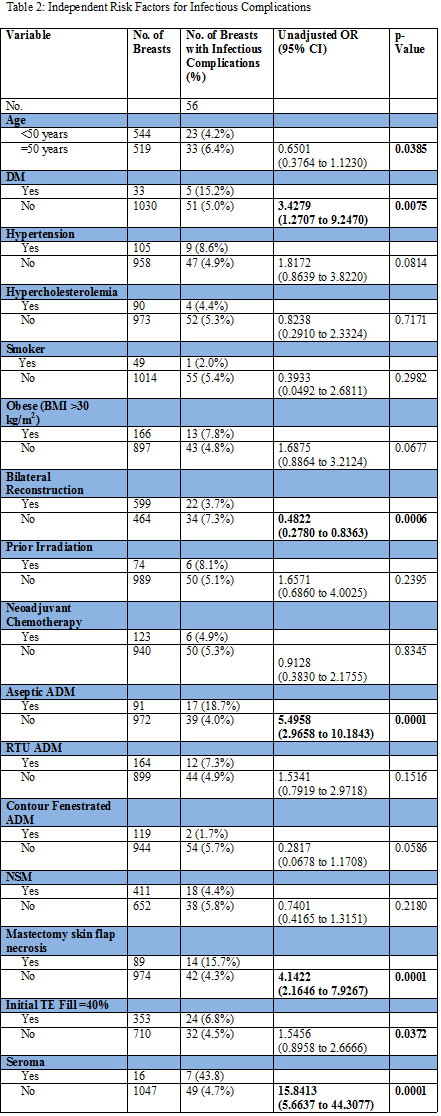
Results: A total of 620 patients (1019 reconstructions) underwent immediate, implant-based breast reconstruction. 8.9%, 16.1%, and 11.7% were performed with aseptic Alloderm, sterile, ready-to-use Alloderm and contour fenestrated Alloderm, respectively (Table 1). Patients with contour fenestrated Alloderm were significantly more likely to have NSM (p=0.0001, 0.0004, 0.0001, respectively) and immediate implant reconstructions (p=0.0001). Those with contour fenestrated Alloderm coverage also had a significantly lesser incidence of infection requiring oral (p=0.0016) and IV antibiotics (p=0.0012) compared to those with aseptic Alloderm coverage. Compared to those with sterile, ready-to-use Alloderm coverage, those with contour fenestrated Alloderm had similar infectious outcomes but significantly more minor mastectomy flap necrosis (p=0.0023). Those with contour fenestrated Alloderm coverage had equivalent infectious outcomes compared to total submuscular coverage but significantly more explantations (p=0.0001) as well as major (p=0.0130) and minor mastectomy flap necrosis (p=0.0001). Diabetes, seroma, mastectomy flap necrosis, aseptic ADM, age of ≥50 years, unilateral reconstruction and TE fill ≥40% were identified as significant independent risk factors for increased infectious complications (Table 2).
Conclusions: Contour fenestrated Alloderm reduces infectious complications compared to aseptic Alloderm and has an equivalent infectious complication profile to sterile, ready-to-use Alloderm and total submuscular coverage.
Back to 2015 Annual Meeting
|
|




