Back to 2015 Annual Meeting
Bipedicled Medial Sural Adipofascial Flap for Coverage of Pretibial Wounds in the Middle Third of the Leg
Oren P. Mushin, MD, Joseph J. Khouri, Jose G. Christiano, MD.
Univeristy of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, NY, USA.
BACKGROUND:
Reconstruction of pretibial wounds in the middle-third of the leg presents a unique challenge. This area features relative paucity of expendable soft tissue. Traumatic injuries may limit availability of cutaneous flaps, disrupt adjacent musculature, and require fixation hardware. The goal of this study was to determine whether a bipedicled medial sural adipofascial flap could be used for coverage of pretibial soft-tissue defects in the middle-third of the leg.
METHODS:
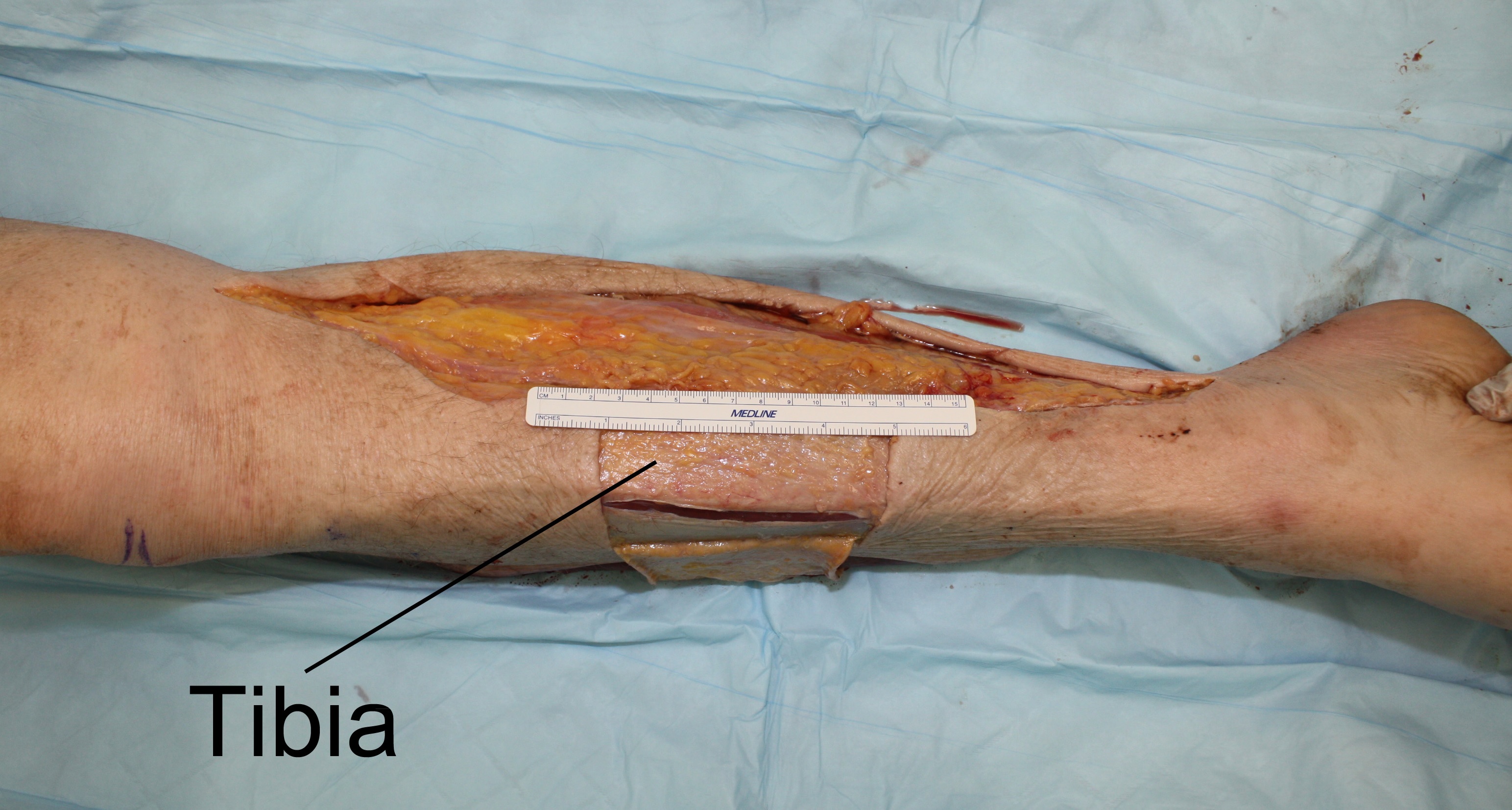
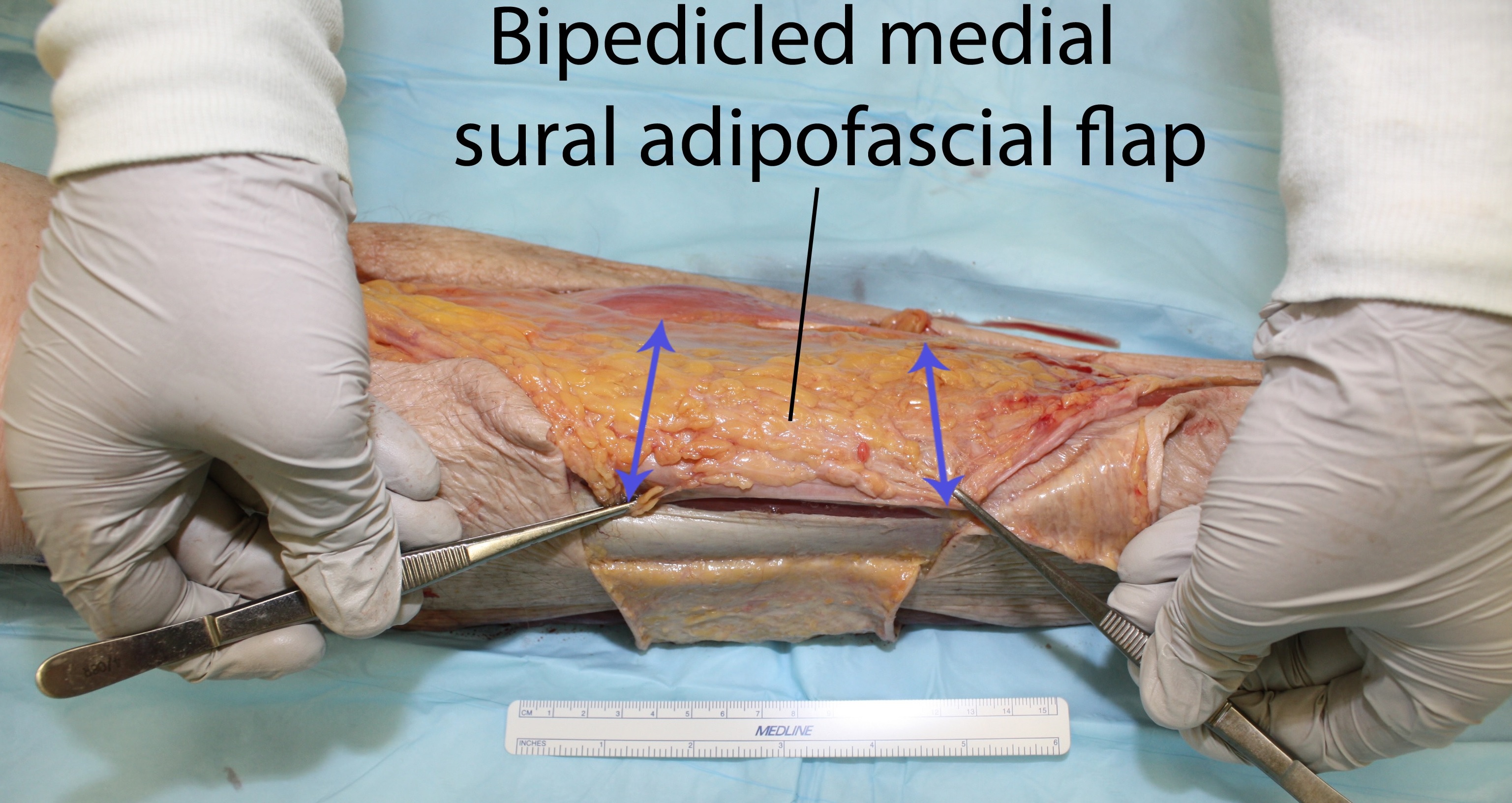
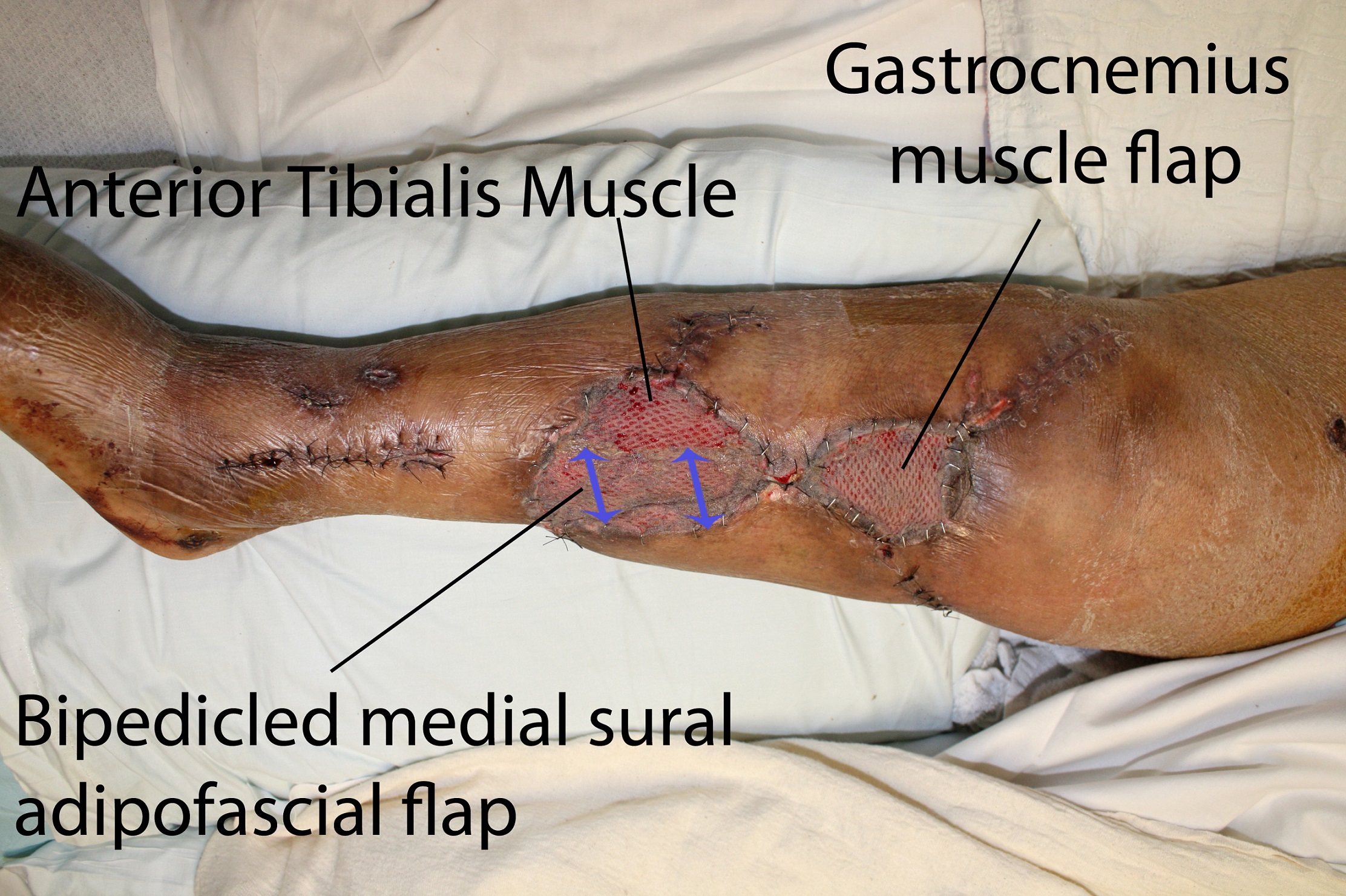
Dissection of three cadaver legs was performed in our laboratory. In each leg, a pretibial soft tissue defect was created involving the entire middle-third of the leg. A bipedicled medial sural adipofascial flap was harvested by extending the cutaneous defect proximally towards the medial condyle and distally towards the posterior edge of the medial malleolus. The leg was undermined medially at the level of Scarpa's fascia. The underlying adipose tissue and sural fascia were incised along the medial tibial border. The adipofascial flap was elevated off the underlying gastrocnemius and soleus muscles and freed posteriorly with a parallel longitudinal fascial incision. The flap was based proximally on the saphenous artery and distally on cutaneous perforators of the posterior tibial artery. It was then advanced antero-laterally to cover the tibia, and secured to the anterior tibialis fascia. Area of tibial bone coverage was measured. This technique was applied in a clinical case. A patient presented with multiple open tibial fractures with soft-tissue loss in the upper two-thirds of the leg, requiring open reduction and hardware fixation.
RESULTS:
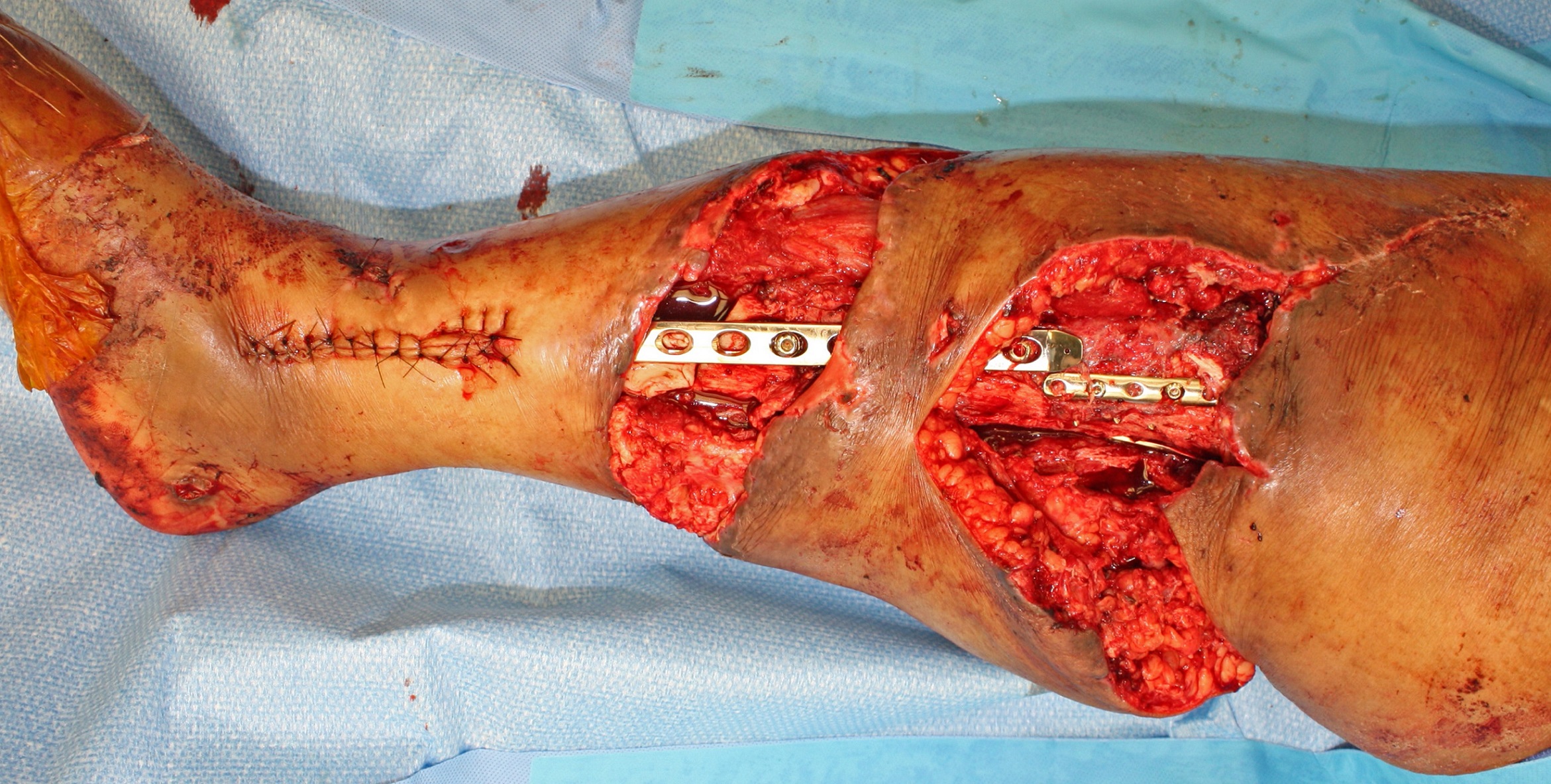
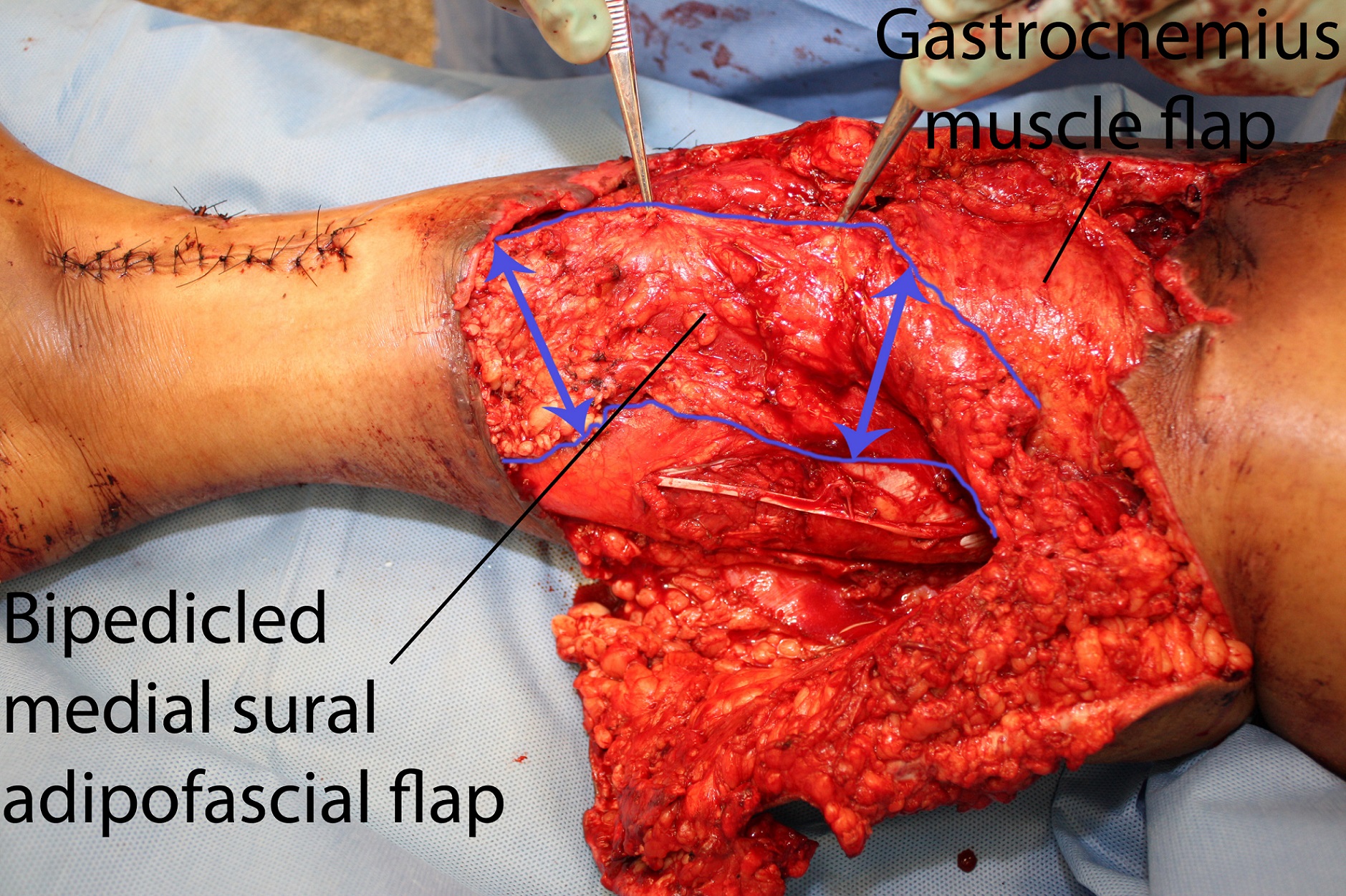
The average pretibial defect created in the cadaver model was 8.5cm in length, encompassing the full tibial width (Figure 1). All defects were successfully covered, with an average length of tibial coverage of 9.2cm (n=3), with minimal tension (Figure 2). In the live patient (Figure 3), the upper-third defect was covered with a medial hemi-gastrocnemius flap. The middle-third defect, spanning 10.3cm, was covered with a bipedicled medial sural adipofascial flap (Figure 4). Skin autografts were applied to both flaps. The leg went on to heal uneventfully (Figure 5).
CONCLUSIONS:
We describe the bipedicled medial sural adipofascial flap and determine that it can successfully cover middle-third pretibial soft-tissue defects. The flap can also be used in conjunction with a gastrocnemius flap for defects involving the upper two-thirds of the leg.
Back to 2015 Annual Meeting
|




