The Benefits of External Tissue Expansion in Complex Extremity Reconstruction: A Case Series
Peter Y.W. Chan1, Chris Michel2, James E. Clune3, Ajul Shah1
1 The Institute for Advanced Reconstruction, Shrewsbury, NJ 2 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Monmouth Medical Center, Long Branch, NJ 3 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
Background: A primary goal of reconstructive wound closure is healthy correction of the wound to previously normal appearance with minimal risk of complications. For reconstruction of large extremity wounds, skin grafting and flap reconstruction are common treatments but associated with a variety of complications.1,2 Comparatively, tissue expansion can provide the opportunity to reconstruct large wounds with native, durable, and sensate tissue without significant donor site morbidity.3,4 Specifically, external tissue expansion is less invasive and avoids complications associated with traditional methods of reconstruction and internal tissue expansion.
Methods: A series of patients with varying wound types and sizes were treated with an external tissue expansion device (DermaClose ®). Device(s) were affixed and left for 7-10 days before closure of the wounds. Outcome was assessed at 2-12 weeks postoperative follow-up.
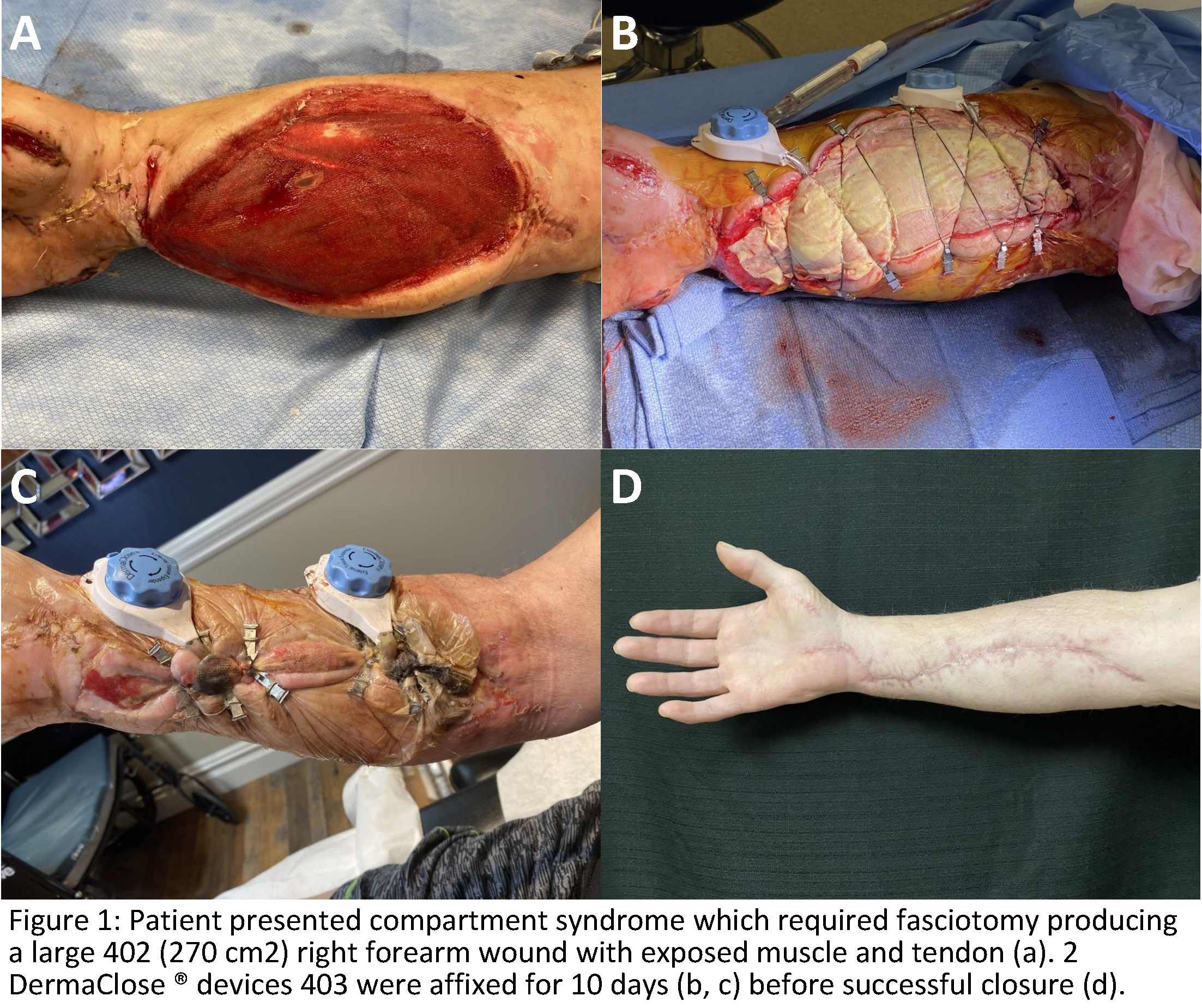
Results: A total of 9 patients were treated ranging in age from 18 to 68 with an average age of 43.6 years (SD + 14.6 yr). Wounds were located on the upper and lower extremities. Wound types included fasciotomy (4), tissue defect due to flap harvest (2), necrotizing fasciitis (1), traumatic amputation (1), and infection (1). Average wound surface area was approximately 228 cm2 (SD = +147.48 cm2), ranging from 80 cm2 (10 x 8cm) to 465 cm2 (31 x 15cm). Exposed structures within the wounds included muscle (7), tendons with paratenon (2), tendons without paratenon (1), and bone (2). All patients had functionally and aesthetically successful closures, demonstrated intact gross sensation in the area of reconstruction, and experienced no major complications.
Conclusions: External tissue expansion is an excellent treatment option in the algorithm of extremity reconstruction as it is efficacious, low cost, and associated with lower complication rates compared with internal tissue expansion, skin grafts, and skin flaps. Plastic surgeons are often called upon as the reconstructive expert with regards to complex extremity reconstruction and should be cognizant of the benefits and versatility of this treatment.
Back to 2021 Posters
