Scoring Model for Predicting Unplanned Readmission After Breast Reduction using National Data
Theresa Webster1, Pablo Baltodano1, Madison Hackley1, Nicholas Elmer2, Briana Kaplunov1, Karen Massada3, Michael Coronado1, Rohan Brebion1, Huaqing Zhao4, Sameer Patel1
1Fox Chase Cancer Center/Temple University Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Philadelphia, PA; 2Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA; 3Mercy Catholic Medical Center Division of General Surgery, Philadelphia, PA; 4Temple University School of Medicine Department of Biostatistics, Philadelphia, PA
BACKGROUND: Reduction mammaplasty continues to be a commonly sought procedure with complication rates ranging from 4.3 to 8.2%. Among elective non reconstructive breast surgery, reduction mammaplasty presents a significantly increased risk of overall morbidity, surgical site infections, and wound disruptions compared to mastopexy and augmentation mammaplasty. Rather than focus only on the preoperative risk factors for complications, as much of the current literature does, we sought to identify the clinical and preoperative risk factors for unplanned readmission within the first post-operative month on a national, multi institutional scale.
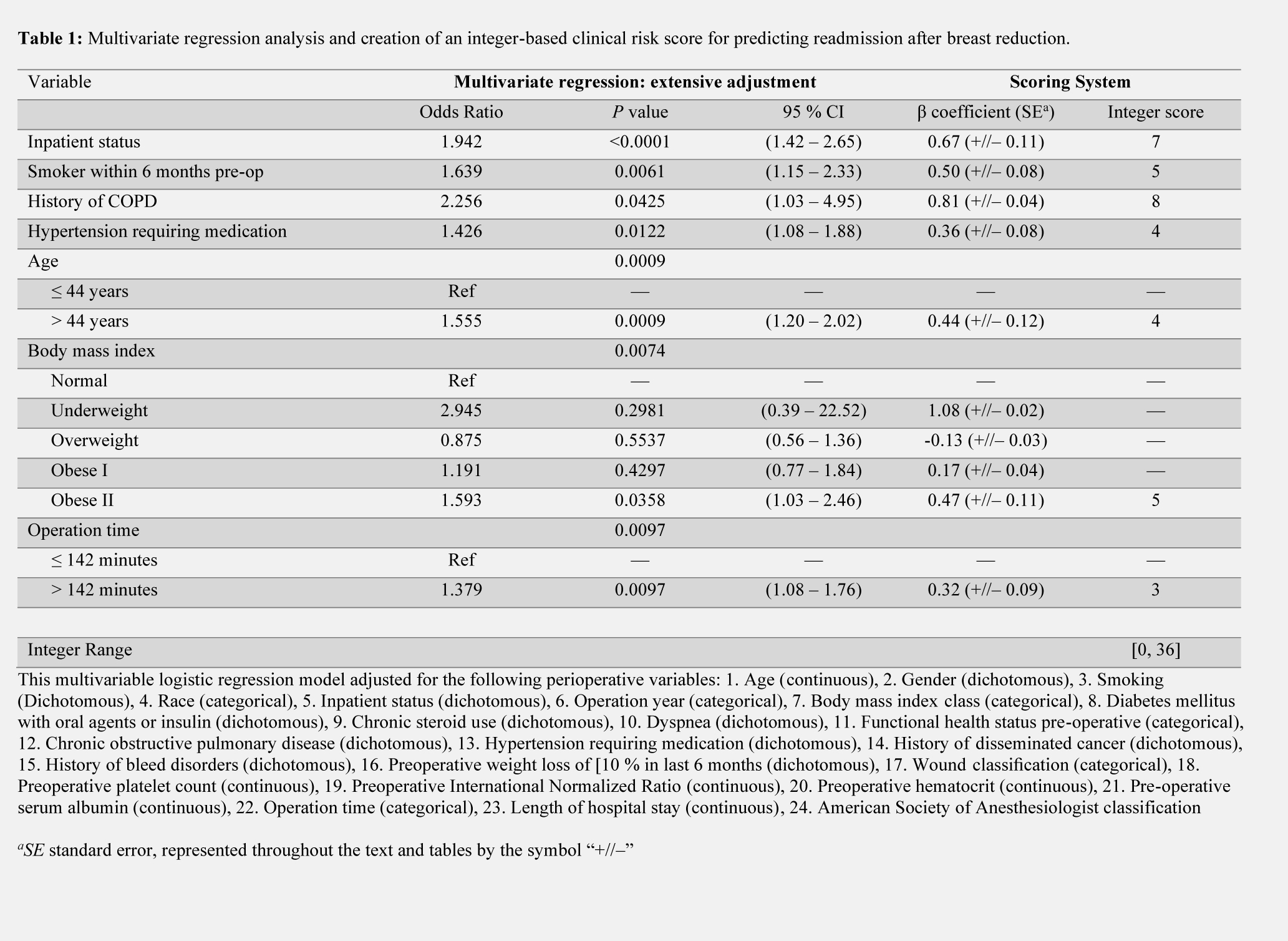
METHODS: Patients who underwent reduction mammaplasty from the ACS-NSQIP 2012 – 2019 database were analyzed to determine rates of reoperation within 30 days of the initial breast surgery. The cohort was divided into 60 and 40% random testing and validation samples. A multivariable logistic regression analysis was then performed to isolate independent factors of unplanned readmission using the testing sample (n = 22,743). The predictors were weighted according to beta coefficients to develop an integer-based clinical risk score predictive of complications. This system was then validated using receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis of the validation sample (n = 15,162).
RESULTS: 37,905 reduction mammoplasties were analyzed. 1.3% (496/37,905) of patients had a hospital readmission in the first 30 post-operative days. Independent risk factors for unplanned readmission included age older than the median of 44 years (p < 0.01), inpatient procedure (p < 0.01), smoking (p < 0.01), hypertension requiring medication (p = 0.01), history of COPD (p < 0.05), BMI greater than or equal to 35 (p < 0.01), and operation time greater than the median of 142 minutes ( p < 0.01). ROC analysis of the validation cohort generated an area under the curve of 0.66, which supports the accuracy of the model.
CONCLUSIONS: This is the first national, multi-institutional study to specifically analyze the independent risk factors associated with hospital readmission following reduction mammaplasty. The scoring model from this data can be utilized not only to improve preoperative planning and identify patients at a higher risk for readmission, but also to decrease unnecessary healthcare costs.
Back to 2021 Posters
