Cost Implications of Enhanced Recovery After Surgery Protocols in Microvascular Breast Reconstruction
Elisa K. Atamian, MD, MS; Rebecca Suydam, BA; Taylor N. Hardy, BA; Mona Clappier, BA; Sarah Barnett, BA; Mark L. Smith, MD; Neil Tanna, MD MBA
Division of Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery, Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, Hempstead, New York
Introduction: Surgical advancements in breast reconstruction have allowed for optimizing patient-reported outcomes and efficiency measures. The Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) protocol has been instrumental in improving outcomes, but the effect of these protocols on healthcare spending has not been examined. This study aims to assess the effect of ERAS protocols on length of hospital stay and costs associated with microsurgical breast reconstruction.
Methods: In 2018, the authors implemented an ERAS protocol for patients undergoing microsurgical breast reconstruction that included all aspects of perioperative care and interventions. Subjects included patients who underwent deep inferior epigastric perforator flap breast reconstruction at the authorsí institution between 2016 and 2019. Data was gathered from the electronic medical record and the hospital systemís finance department and patients were divided into pre-ERAS (2016, 2017) and ERAS (2018, 2019) cohorts. A Two-Sample T-test was used for statistical analysis.
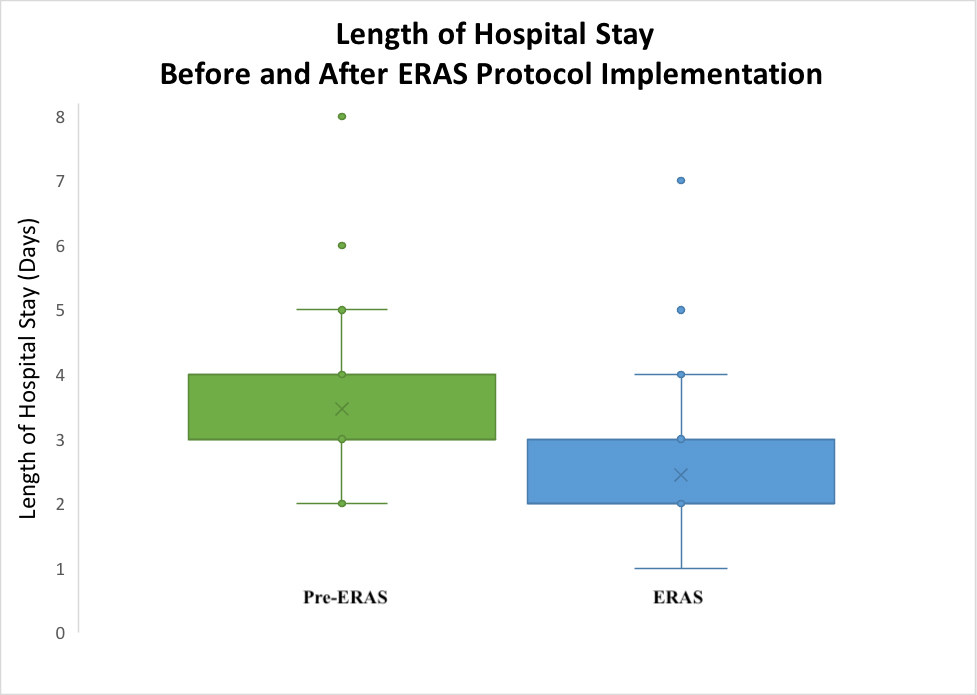
Results: The study included 269 patients with no statistically significant differences in demographic data between the cohorts. The average length of hospitalization was 3.46 days for the pre-ERAS group and 2.45 days for the ERAS group (p=0.000). In a linear regression model, the ERAS protocol predicted a 1.04 day decrease in the length of stay (p=0.000). The ERAS cohort demonstrated cost reductions in all categories including room and board (-18.5%), pharmacy (-4.5%), surgery labor (-11.8%), and postoperative care labor (-30.8%).
Conclusion: The rising cost of healthcare presents a challenge for providers to reduce the cost burden placed on our health system while providing the highest quality care. This study demonstrates that the use of standardized ERAS protocols can achieve this two-fold goal.
Back to 2022 Abstracts