Therapeutic Targeting of Protein Homeostasis Defects in Venous Malformations
Averill Clapp*1, Samantha A. Kaplan2, Carrie J. Shawber3, June K. Wu2
1Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York, NY; 2Department of Surgery, Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY; 3Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY
Venous malformations (VMs) are congenital vascular lesions that cause severe morbidities and have no cure. Pathogenic PIK3CA variants have been identified in VM endothelial cells (VMECs). PI3K pathway inhibitors have been used to target VMECs, but clinical response is incomplete. We found that proteasome inhibitors (PIs), which target cells with proteostasis defects, significantly reduced VMEC growth compared to current therapies. We hypothesize that pathogenic PIK3CA variants result in proteostasis defects which are targeted by PIs, resulting in VMEC cell death.
Human microvascular endothelial cells (HMVECs) were infected with lentiviruses encoding pathogenic PIK3CAH1047R (HMVEC:PIK3CAH1047R) or empty vector (HMVEC:EV) and co-stained for the proteasome 20S subunit (PSMB5) and EC cell surface protein CD31. HMVECs and patient-derived VMECs with PIK3CA variants (n = 2) were treated with vehicle or 100 nM (subclinical dose) of PI oprozomib (OPZ) for 6h and stained for CD31 and VECADHERIN; cell death was assessed by TUNEL assay in vehicle-, 100 nM OPZ-, and 1 uM (clinical dose) OPZ-treated HMVECs and VMECs. Quantification was performed with ImageJ. Statistical analysis was performed with ANOVA and post-hoc Tukey test, with p < 0.05 as significant.
HMVEC:PIK3CAH1047R had increased CD31/PSMB5 colocalization relative to HMVEC:EV (Figure 1A). Compared to vehicle-treated VMECs, OPZ-treated VMECs had significantly increased CD31 and VE-cadherin protein levels (Figure 1B). In contrast, OPZ-treated HMVECs did not have increased protein accumulation. OPZ induced cell death in VMECs but not HMVECs (Figure 1C,D).
Patient-derived VMECs with PIK3CA variants and HMVEC:PIK3CAH1047R exhibit dysregulated protein trafficking. OPZ treatment exacerbated cytoplasmic protein accumulation in VMECs but not HMVECs. Both subclinical and clinical doses of OPZ induced significant cell death in VMECs but not HMVECs, suggesting PI specificity against pathogenic cells. The proteasome degradation pathway may be a promising therapeutic target for VM patients.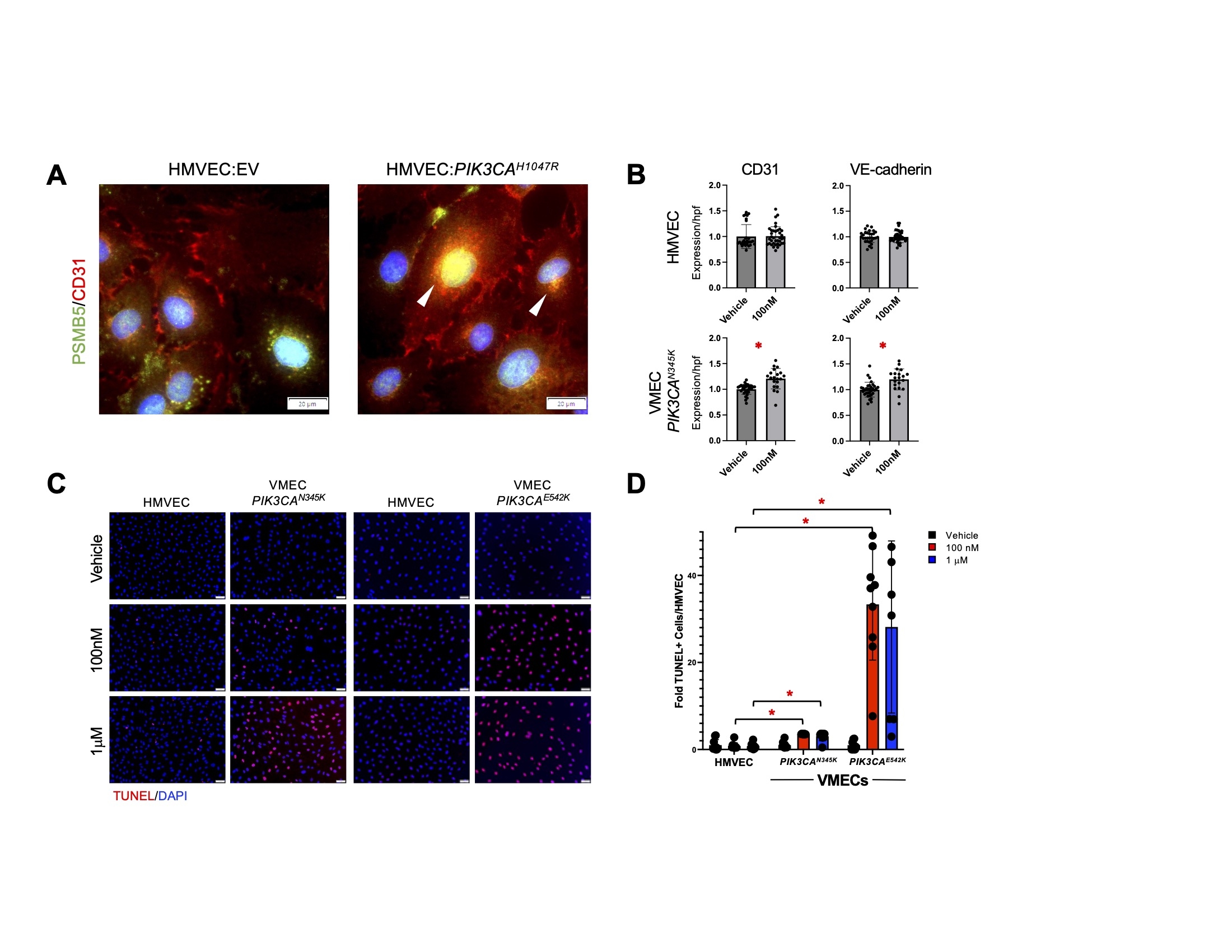
Figure 1. PIK3CA hyperactivation in ECs increased CD31 expression, CD31 colocalization with proteasome, and cell death in response to proteasome inhibitor. (A) Human microvascular endothelial cells (HMVECs) transfected with empty vector (EV) and hyperactivated PI3K variant PIK3CAH1047R were co-stained for proteasome 20S subunit (PSMB5) (G) and CD31 (R). Arrowheads mark select areas of colocalization. (B) CD31 and VE-cadherin protein levels in vehicle- and 100 nM oprozomib (OPZ)-treated cells. *p < 0.0001. (C) TUNEL assay of vehicle-, 100 nM OPZ-, and 1 uM OPZ-treated HMVECs and venous malformation endothelial cells (VMECs) with PIK3CA variants. (D) Quantification of TUNEL-positive nuclei relative to HMVEC in vehicle-, 100 nM OPZ-, and 1 uM OPZ-treated VMECs with PIK3CA variants. *p < 0.0001. Error bars represent standard errors of the means.
Back to 2023 Abstracts


