Nationwide Analysis of Out of Pocket Costs And Variation for Autologous and Implant Based Reconstruction
Olachi Oleru*, Nargiz Seyidova, Sarah Nathaniel, Martina Brozynski, Nikita Roy, Anais Di Via Ioschpe, Lior Levy, Peter J. Taub
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY
Many factors influence a patient's decision to undergo autologous versus implant-based breast reconstruction, including medical, social, and financial considerations. This study aims to investigate differences in out of pocket and total spending for patients undergoing autologous and implant-based breast reconstruction.
The IBM MarketScan Commercial Database was queried to extract all patients who underwent autologous or implant based breast reconstruction from 2017 to 2021. Financial variables included gross payments to the provider (facility and/or physician) and out of pocket costs (total of coinsurance, deductible, and copayments). Univariate and mixed-effects linear regression was utilized to analyze parametric contributions to total gross and out of pocket costs.
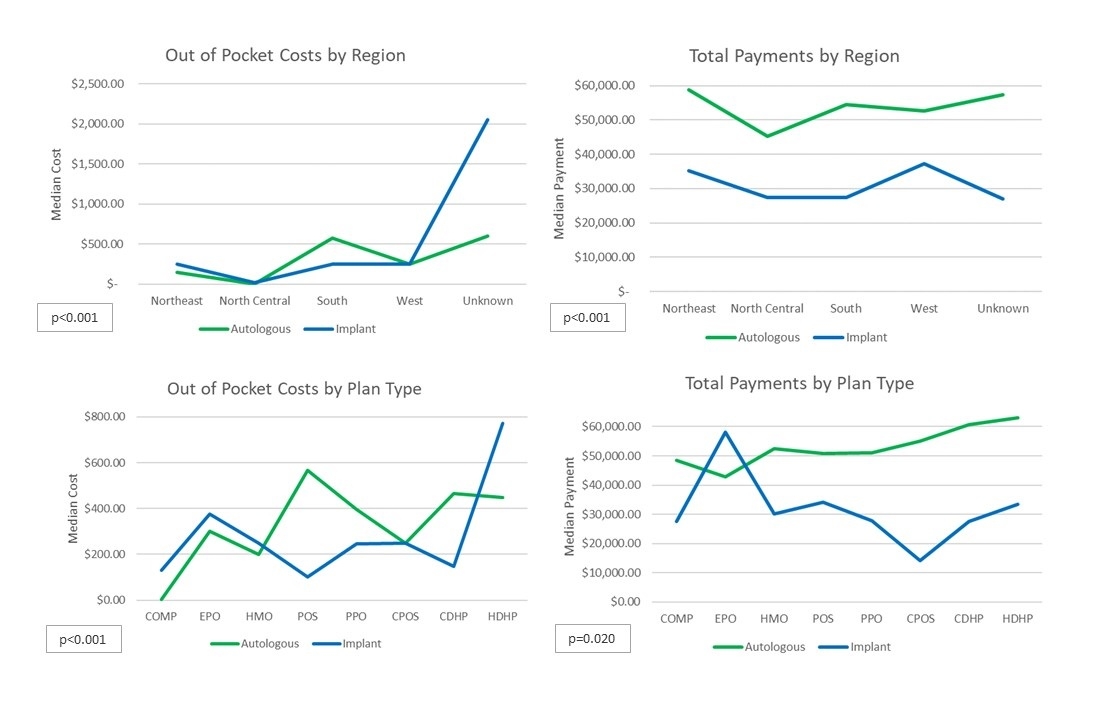
This sample identified 2,151 autologous breast reconstruction and 426 implant-based breast reconstruction episodes. The median total gross payments were greater for autologous reconstruction ($52,325.40 vs. $28,362.23, p<0.001). Median out of pocket costs were also higher for autologous reconstruction than implant-based reconstruction ($323.41 vs. $250.00, p=0.017), most pronounced in the South region. The majority of patients in both groups had employer insurance (72.4% and 74.9%). Regression analysis revealed that autologous reconstruction (versus implant-based) contributes significantly to increasing out of pocket costs (B = $413.91, p=0.041) and increasing total costs (B = $32,316.38, p<0.001). Type of health plan was significantly associated with increasing total costs (B = $11,312.52, p<0.001), but not with out of pocket costs.
The US national data demonstrate that autologous breast reconstruction has higher out of pocket costs and higher gross payments than implant-based reconstruction. Most of the variation in out of pocket costs were concentrated in the South. More study is needed to determine the extent to which these financial differences affect patient decision making, and to what extent regional economic factors affect insurance coverage.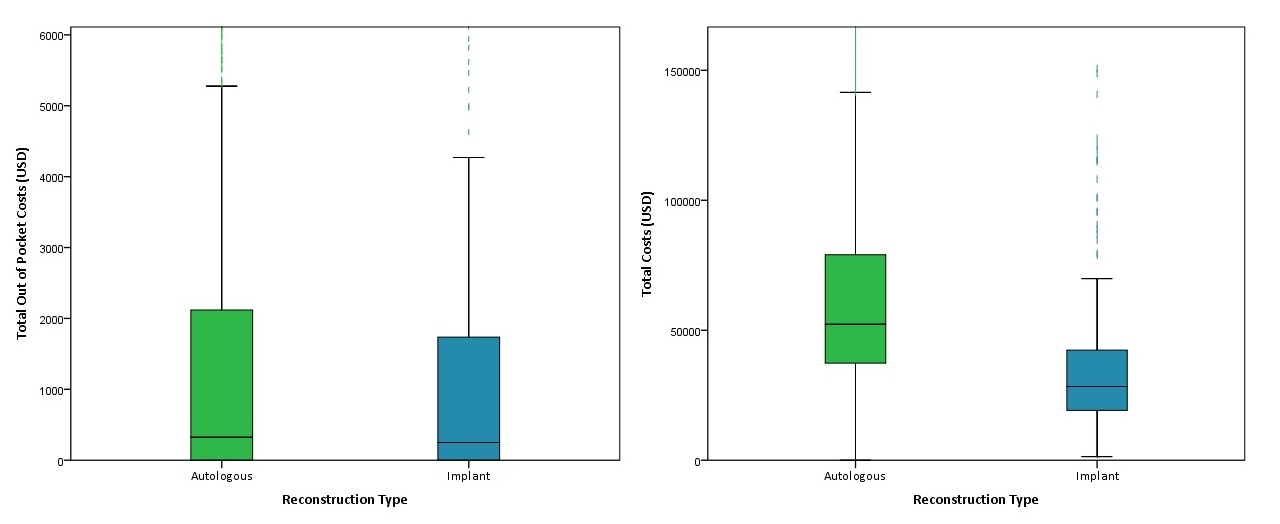
Back to 2023 Abstracts


