Sagittal Sinus Micropuncture to Induce Scaffold Vascularization
Jessica C. El-Mallah*1, Summer N. Horchler1, Olivia Waldron1, Mingjie Sun1, Elias Rizk2, Dino J. Ravnic1
1Department of Surgery, Penn State Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, Hershey, PA; 2Department of Neurosurgery, Penn State Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, Hershey, PA
Bone flaps replaced after craniectomy often fail due to poor re-vascularization. We have described a microsurgical approach termed micropuncture (MP), which disrupts the blood vessel wall to provide a route for cellular extravasation and more rapid vascularization. We observed that venous MP can promote scaffold vascularization in a rat hindlimb model. Here we hypothesized that MP of the sagittal sinus vein (SSV) would result in a greater degree of scaffold vascularization as compared to non-MP controls.
An 8mm calvarial defect was created in rats. 60um SSV MPs were made at 1mm intervals over an 8mm length prior to collagen scaffold implantation. Controls were without MP. At Day 7 animals underwent in situ fluorescence angiography and scaffolds were explanted. Explants were prepared for whole mount and thin section histology. Luminal formation was manually counted from trichrome sections. Endothelial cell (CD31) infiltration was assessed with immunofluorescence and quantified with ImageJ software (Bethesda, MD). Vascular metrics were quantified using artificial intelligence (AI; MetaVi Labs; Austin, TX) from whole mount angiograms.
No adverse events were noted. At Day 7 MP gross scaffolds showed increased vascularization compared to controls (Figure 1 A,B). This was corroborated by mean luminal counts on trichrome sections (12.3 vs 3.95 per HPF; p<0.002; Figure 1 C-F). Increased CD31 staining area was observed within MP scaffolds (2.9% vs 0.12% per HPF; p<0.006; Figure 1 G,H). Whole mount angiography demonstrated higher mean vascular density in MP scaffolds (10.64% vs 1.82% per HPF; p<0.02; Figure 1 I,J). MP scaffolds showed increased branch counts (17.74 vs 1.89 per HPF; p< 0.002), loop counts (9.11 vs 1.11 per HPF; p<0.02) and vessel diameters (34.64 um vs 20.79 um; p<0.004).
In a rat model, MP of the SSV appears safe and elicits a localized pro-angiogenic environment. This suggests MP can be used across anatomic sites to expedite implant vascularization. Ongoing work will determine its utility in bone flap re-vascularization and survival following craniectomy.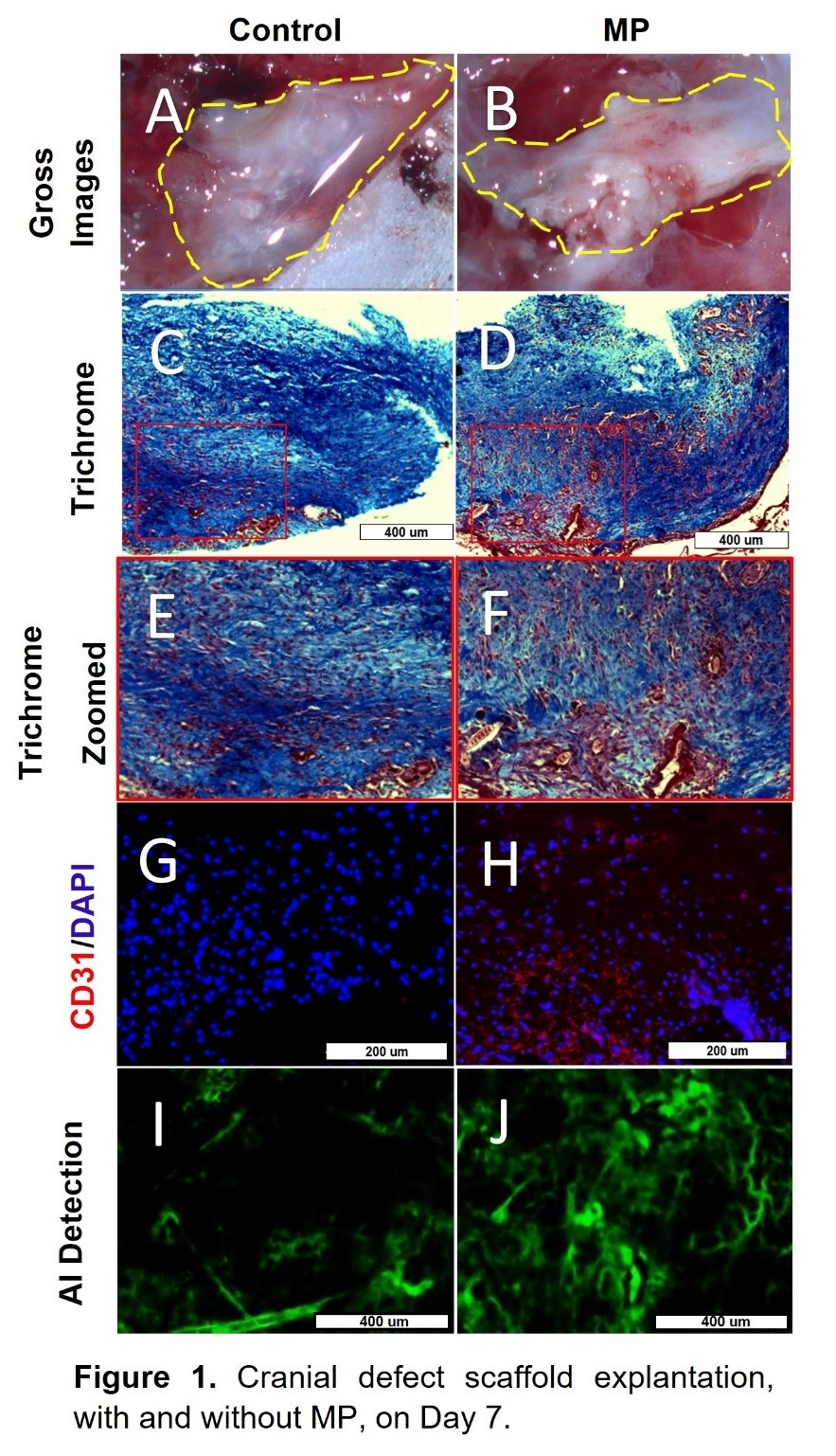
Back to 2023 Abstracts


