A Novel Patient Decision Aid for Breast Reconstruction: A Pilot Study
Donovan R. White*1, Richard Poulton1, Lillian Boe2, Jonas Nelson1, Carrie Stern1
1Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, Hueytown, AL; 2Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Memoriall Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY
Many women undergoing mastectomy feel overwhelmed regarding the breast reconstruction information provided to them. Three dimensional(3D) interactive technology has been shown to be a valuable tool in enhancing patient education. Knowing these benefits, we developed a prototype of an interactive 3D decision support tool for women. We conducted a pilot study to assess the feasibility of implementation of this decision support tool during breast reconstruction consultation.
Patients were randomized into an experimental(3D decision support tool and standard of care) or control group(standard of care alone) and they completed BREAST-Q satisfaction with information and satisfaction with breasts, the decision regret scale, and the decision quality index. These were completed immediately after consultation and at 4-weeks and 3-months postoperatively(PO).
Sixty-four patients were included(31 experimental, 33 control). 84% of patients underwent implant-based reconstruction. There were no significant findings between groups throughout respective timepoints. Mean satisfaction with information scores were similar in the experimental group(mean 54, 95% CI 52, 56) and control group(mean 52.9, 95% CI 50, 56) at 4 weeks, and 3-months PO. In the experimental group, a significant increase in mean knowledge scores from baseline(mean 60, 95% CI 52, 68) to post-consultation(mean 69, 95% CI 63, 76; p=0.03) was seen that was not present in the control group. Finally, there was a significant decrease in decision regret for the experimental group from after consultation(mean 20, 95% CI 14, 26) to 4-weeks(mean 10, 95% CI 3.7, 16; p=0.007) and 3-months(mean 11, 95% CI 5.3, 16; p=0.01), which was not seen in the control.
3D decision support incorporation for breast reconstruction during consultation is feasible. Experimental group patients reported less decision regret and improved knowledge. Future work will include a well-powered study to further define the impact of an interactive decision aid for post mastectomy reconstruction.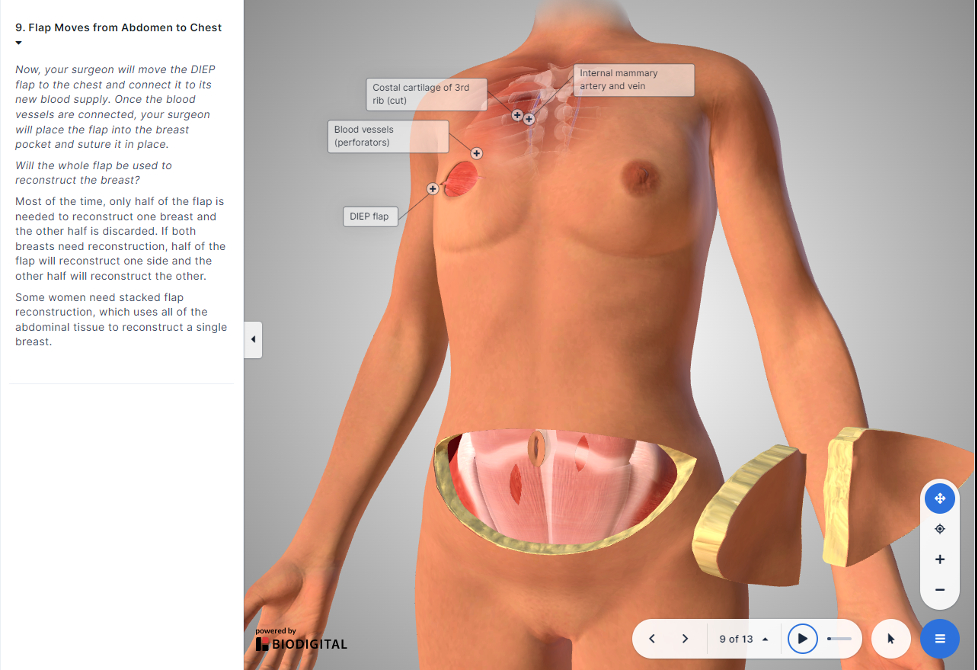
Back to 2023 Abstracts


